CUDA Parallel Programming/ProjectDescription: Difference between revisions
No edit summary (change visibility) |
No edit summary (change visibility) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Definition of SNP-Genes == |
== Definition of SNP-Genes == |
||
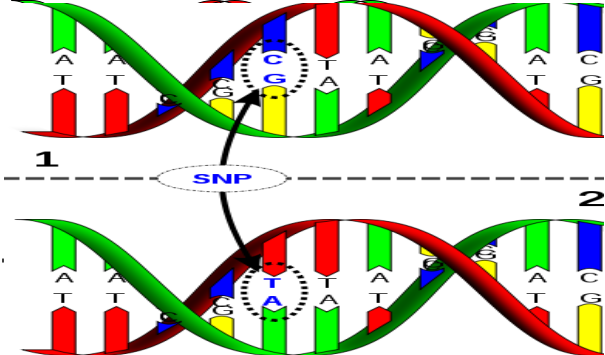
Single nucleotide polymorphisms are DNA sequence variations which occur when a single nucleotide (A, T, C, and G) in the genome sequence is obtained. For example a SNP (bad-gene) may change the DNA sequence TAGGCTAA to TTGGCTAA. For a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. The changed gene is represented as bad-gene. |
Single nucleotide polymorphisms are DNA sequence variations which occur when a single nucleotide (A, T, C, and G) in the genome sequence is obtained. For example a SNP (bad-gene) may change the DNA sequence TAGGCTAA to TTGGCTAA. For a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. The changed gene is represented as bad-gene. |
||
//pic |
|||
[[File:Pic.png]] |
|||
Although more than 99% of human DNA sequences are equal to each other. Less than 1% percent difference in the DNA sequence of humans may result how humans respond to |
Although more than 99% of human DNA sequences are equal to each other. Less than 1% percent difference in the DNA sequence of humans may result how humans respond to |
||
disease; viruses, bacteria, toxins, drugs, chemicals and therapies. This shows each unique characteristics of human body. This makes SNPs valuable for biomedical research and for developing medical diagnostics. Today scientists believe that SNP can guide us to identify the multiple genes that are responsible of illnesses such as; cancer, diabetes, vascular disease, and some forms of mental illness. SNPs do not cause disease, but they can help determine |
disease; viruses, bacteria, toxins, drugs, chemicals and therapies. This shows each unique characteristics of human body. This makes SNPs valuable for biomedical research and for developing medical diagnostics. Today scientists believe that SNP can guide us to identify the multiple genes that are responsible of illnesses such as; cancer, diabetes, vascular disease, and some forms of mental illness. SNPs do not cause disease, but they can help determine |
||
Revision as of 04:08, 15 May 2012
CUDA / FastAnova
Introduction
CUDA stands for Compute Unified Device Architecture and is a new hardware and software architecture for issuing and managing computations on the GPU as a data-parallel computing device without the need of mapping them to a graphics API. CUDA includes a programming model along with hardware support that simplifies parallel implementation. CUDA is one of the main programming languages that increase the speed of result more than any other languages. Programmers need training in parallel programming to be fully effective in computer science. CUDA forms a platform that contains both high-performance applications for heterogeneous platforms that contain both central and graphics processing units. Data-parallel processing maps data elements to parallel processing threads. Many applications that process large data sets such as arrays can use a data-parallel programming model to speed up the computations. In that case I aimed to use CUDA in order to do a helpful analyze on the medical area (bad-genes). As a first step I search a string under a 1 Mb of a text file under parallel programming. My aim was to observe how parallel programming might increase the performance of the process.
Definition of SNP-Genes
Single nucleotide polymorphisms are DNA sequence variations which occur when a single nucleotide (A, T, C, and G) in the genome sequence is obtained. For example a SNP (bad-gene) may change the DNA sequence TAGGCTAA to TTGGCTAA. For a variation to be considered a SNP, it must occur in at least 1% of the population. The changed gene is represented as bad-gene.
Although more than 99% of human DNA sequences are equal to each other. Less than 1% percent difference in the DNA sequence of humans may result how humans respond to
disease; viruses, bacteria, toxins, drugs, chemicals and therapies. This shows each unique characteristics of human body. This makes SNPs valuable for biomedical research and for developing medical diagnostics. Today scientists believe that SNP can guide us to identify the multiple genes that are responsible of illnesses such as; cancer, diabetes, vascular disease, and some forms of mental illness. SNPs do not cause disease, but they can help determine
someone, who will develop a particular illness. Which will help researchers find genes associated with human disease.
Research Description
Main Purpose of The Project
The purpose of this research project is to illustrate the performance that can be gained by using GPUs in general purpose computing compared to the performance that can be gained by using CPUs.
My project is main aim is to help medical area and man-kind. Main purpose is to analyze genes in order to find and analyze SNP genes. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are an important problem in area of biology. ANOVA (analysis of variance) test is routinely used in analyzing SNP genes. Fast-ANOVA method implemented in order to perform ANOVA test on SNP-pairs in a batch mode, which supports large permutation test, and faster method of ANOVA. FastANOVA is orders of magnitude faster than the brute-force implementation tests on all SNP pairs. Related to result it obtain from SNP-genes dataset conclude how bad-genes can result human or animals’ unique characteristics. SNP –genes are the less than %1 of different genes that will define personality of each person. For example by comparing the genes of people under a gene pool dataset, we are able to obtain different genes that may cause unique characteristic of each human being such as; hair color, length, skin color etc. By doing and analyzing that we are able to determine someone, who will develop a particular illness and its unique characteristics. Genetic definition, that our gene-structure are contain a long huge of data. If we sequential compare each person’s gene code separately it will take a lot of time. If we implement FastANOVA algorithm in a parallel computing it will help us to obtain our result much faster and obtain much more reliable and correct results. Under this condition, my project aims to implement parallel computing under CUDA that parallel analyze the huge data set of genes in an efficient and fast way. It would be a great tool for scientists to obtain a robust, reliable and fast result from millions of people and the very long DNA-sequence.
Why more speed or Parallelism in Programming and on Future?
The main motivation for massively parallel programming and my project by using CUDA is for applications to enjoy a continued increase in speed in future hardware generations. By doing parallel execution, a good implementation on a GPU can achieve more than 100 times (100x) speedup over sequential execution. Data parallelism may achieve 10 x speeds up the sequential code. When number of parallel working threads increase in a piece of code the speed-up developed related to that increment. The CUDA programming model is implemented in order to cover a much section of code-pieces of the exciting applications. In today’s rapidly increasing technology biological research community is moving more into the molecular biology. As a first part in my project my aim was to understand and prove has parallelism may increases the speed of the program. In order to do this, I aim to read a 1 Mb of text document under parallel structure and under parallel thread search a string under each block, which is analyze a large data set parallel instead of sequential analyzing. In order to get maximum benefit from CUDA, I firstly focus on finding ways to parallelize sequential code, which are mainly excessive transfers between the host and the device. No data parallelism is implemented in the host code (CPU). Rich amount of data parallelisms are implemented in the device code (GPU). Example from an exercise I have done. Each block is searching a string “b” under a block. Each block compares this string with the dependent data that they are related. Firstly I set that each block is composed by data set that is formed by 100 characters. If all text file has 500 characters, there will be 5 blocks, each contains 100 characters. After I compile my program, it is able to search and find character in the GPU side by analyzing data in small sets. After I have found the search string indexes on GPU, I have returned my result into CPU. On my second step I have implemented data size as 50, which will increase the number of block which cause increase in the number of parallel computing. As a result number of blocks has increased. As a first and introduction step into my project, I was able to search a database that is divided into data pieces. Each piece is analyzed as a parallel-computing. My first and most important goal was to perform parallel programming reliability CUDA programming focus on that my project will achieve character in for and functionality. correct mainly data parallelism, both high performance and high reliability. More parallel code results faster code to run.
__global__ void square_array(struct parallelText* mylines, int *I, int N){int idx = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;char *searchedTxt = mylines[idx].data;int linelen = mylines[idx].length;char a[0];memcpy(a, "alper", 5);
int flag = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < linelen; i++){
if(searchedTxt[i] == a[0] && searchedTxt[i+1] == a[1] && searchedTxt[i+2] == a[2]){
atomicAdd((I + idx), 1); //atomicly incremented
}
}
} __global__ void settingResultArray(struct parallelText* mylines, int *R, int N ) {
int idx = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
char *searchedTxt = mylines[idx].data; int linelen = mylines[idx].length;
char a[0]; memcpy(a, "alper", 5);
int flag = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < linelen; i++){
if(searchedTxt[i] == a[0] && searchedTxt[i+1] == a[1] && searchedTxt[i+2] == a[2]){
int temp = atomicAdd(&gpu_Count, 1);
R[temp] = idx * DATALEN + i;
}
}
}
Conclusion
The main goal of my project is to build up FastANOVA on CUDA programming. FastANOVA is used for genome-wide ANOVA test. It guarantees to find the optimal solution. Experimental results show that FastANOVA 2 to 3 times faster than the alternative algorithm. With the help of CUDA, it will be much faster. As a result with the help of this project large number of SNPs can be find with the less amount of time and more efficiently.
References:
- [0] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computational_science
- [1] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Dna-SNP.svg
- [2] Programming Massively Parallel Processors, David B.Kirk & Wen-mei W.Hwu
- [3] CUDA by example An Introduction to General-Purpose GPU Programming, Jason Sanders and Edward Kandrot
- [4] Rauber T., Rünger G., “Exploiting Multiple Levels of Parallelism in Scientific Computing”. IFIP International Federation for Information Processing, 2005, Volume 172/2005, 3-19, DOI: 10.1007/0-387-24049-7_1
- [5] NVIDIA Tesla GPU Computing Technical Brief. Version 1.0.0, 5/24/2007
- [6] Ackermann, J., Baecher, P., Franzel T., Goesele, M., Hamacher, K., “Massively-Parallel Simulation of Biochemical Systems”
- [7] Davis, J., Ozsoy, A., Patel, S., Taufer, M., “Towards Large-Scale Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Graphics Processors”
- [8] Rodríguez, A., Trelles, O., Ujaldón, M., “Using Graphics Processors for a High Performance Normalization of Gene Expressions”
- [9] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cluster_analysis
- [10] Domany, Eytan. “Cluster Analysis of Gene Expression Data”
- [11] http://www.nvidia.com/object/what_is_cuda_new.html